Niacinamide: 4 Benefits for Skin and Usage Tips for Topical Use
by elmt Lab on Mar 22, 2023

Niacinamide is a versatile and gentle skincare ingredient that is known for its many benefits. It can improve hyperpigmentation, regulate sebum production, strengthen the skin barrier, and provide antioxidant protection. Here are some additional things to note when using this powerful ingredient in your routine.
What is Niacinamide?
Niacinamide, also known as vitamin B3, is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for our skin health. It is found in foods like meat, fish, and leafy green vegetables, but can also be applied topically to the skin.
Niacinamide is a multitasking ingredient that has been extensively studied for its benefits on the skin. It can help to brighten skin tone, improve fine lines and wrinkles, and control sebum production. Additionally, it has antioxidant properties that protect the skin from environmental stressors and can reduce inflammation.

How Does Niacinamide Benefit the Skin?
When applied topically, niacinamide is great for a number of reasons.
1. Helps Reduce Hyperpigmentation: Pigmentation occurs when melanocytes in the outer layer of our skin produce melanin, a pigment responsible for protecting our skin from ultraviolet rays, and the color of our skin. Stimulation from ultraviolet rays induces production of melanin, which is then stored and transported by melanosomes to surrounding skin cells.

Niacinamide prevents the movement of these melanin pigments, and studies have shown that it can reduce melanin pigment migration by 35-68%, therefore helping to relieve excessive skin pigmentation [1].
Additionally, an eight week study on the effects of a 4% niacinamide cream in treating women with melasma shows it was effective in treating about 40% of participants [2].
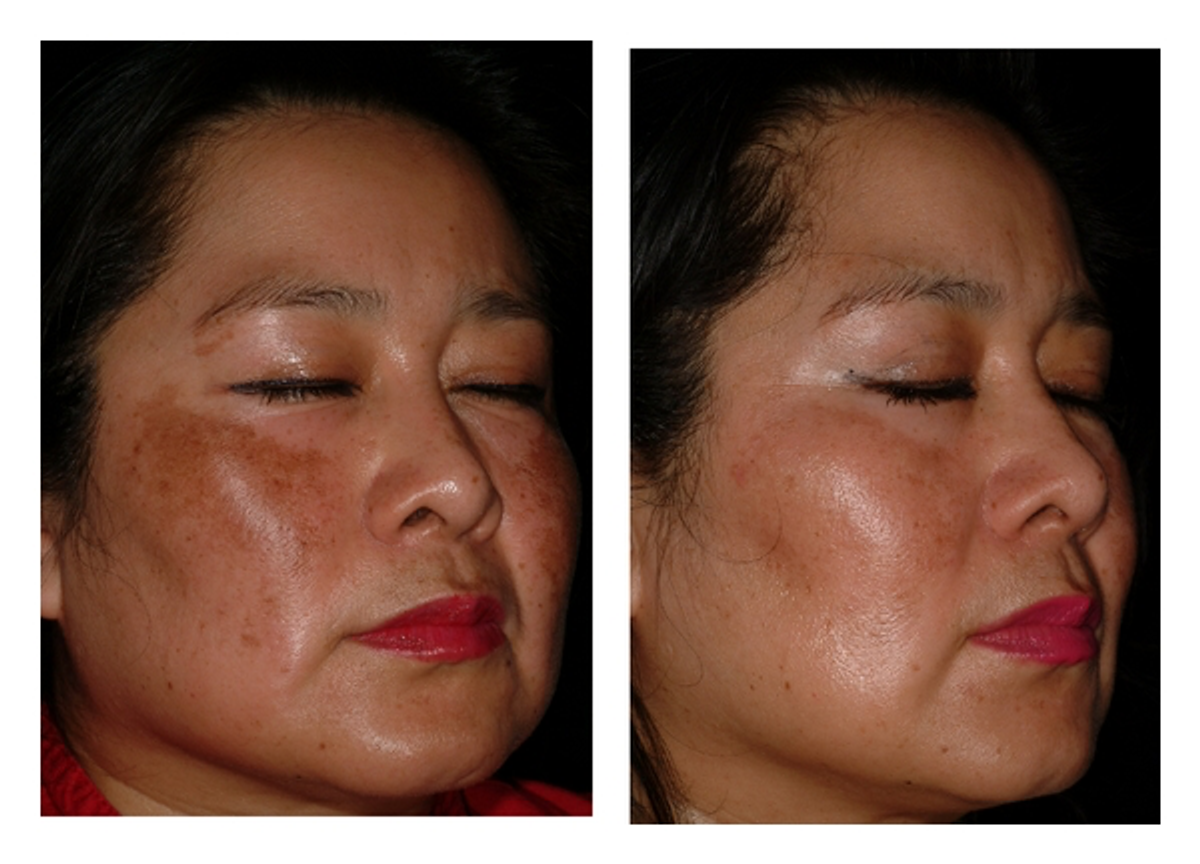
2. Antioxidant Properties: Niacinamide has antioxidant properties that can protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals, and can even protect skin cells from oxidative stress caused by air pollution [3].
3. Regulates Sebum Production: Sebum, an oil produced by the skin's sebaceous glands, is essential for healthy skin. However, overproduction of sebum can cause clogged pores and acne. Fortunately, niacinamide can help regulate sebum production by reducing the activity of sebaceous glands. In fact, a study found that applying a moisturizer containing 2% niacinamide resulted in lower sebum production and excretion rates [4]. This makes niacinamide a promising ingredient in skincare products for those struggling with excess sebum production and its related issues.
4. Strengthens Skin Barrier: Maintaining a healthy skin barrier is crucial for individuals with sensitive or inflamed skin. Fortunately, niacinamide can help strengthen the skin barrier. In a study involving 50 subjects with rosacea, applying a moisturizer with niacinamide for four weeks improved keratin barrier function and alleviated symptoms such as dryness and peeling [5]. This highlights the potential benefits of using niacinamide in skincare products for those with compromised skin barriers.
Niacinamide: Effective Use
If you're interested in incorporating niacinamide into your skincare routine, there are a few things to keep in mind for effective use:
1. Check the Concentration: When it comes to the safety and efficacy of niacinamide, the concentration matters. For optimal results, look for products that contain at least 2% niacinamide. According to data published by the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR), concentrations between 2-5% are unlikely to irritate the skin. However, it's important to consult a dermatologist before using products with a niacinamide concentration greater than 5%.
… A usage test involving 159 females with a cream containing 2% niacinamide resulted in no negative reactions. A 21-day cumulative irritation test in 25 subjects at niacinamide concentrations up to 5% resulted in no irritancy.
2. Use with Sunscreen Niacinamide remains stable in the sun and even has protective effects against ultraviolet damage caused by sun exposure. To maximize its benefits, consider using products containing niacinamide during your daytime skincare routine in conjunction with sunscreen.
Sources
[1] T. Hakozaki, L. Minwalla, J. Zhuang, et el., The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer, British Journal of Dermatology , Volume 147, Issue 1, 1 July 2002, Pages 20–31.
[2] Josefina Navarrete-Solís, Juan Pablo Castanedo-Cázares, Bertha Torres-Álvarez, et el., A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma, Dermatol Res Pract. 2011; 2011: 379173.
[3] Ao Xuan Zhen, Mei Jing Piao, Kyoung Ah Kang, et el., Niacinamide Protects Skin Cells from Oxidative Stress Induced by Particulate Matter, Biomolecules & Therapeutics 2019; 27(6): 562-569
[4] Zoe Diana Draelos 1, Akira Matsubara, Kenneth Smiles, The effect of 2% niacinamide on facial sebum production, J Cosmet Laser Ther . 2006 Jun;8(2):96-101. doi: 10.1080/14764170600717704.
[5] Zoe Diana Draelos 1, Keith Ertel, Cindy Berge, Niacinamide-containing facial moisturizer improves skin barrier and benefits subjects with rosacea, Cutis . 2005 Aug;76(2):135-41.












